Android carservice架构及启动流程
文档内容:carservice架构介绍,内容有Car APP、Car API、Car Service等部分,carservice启动流程
1. 概述
1.1. 架构
Google官网上介绍汽车架构:
车载HAL是汽车与车辆网络服务之间的接口定义(同时保护传入的数据):
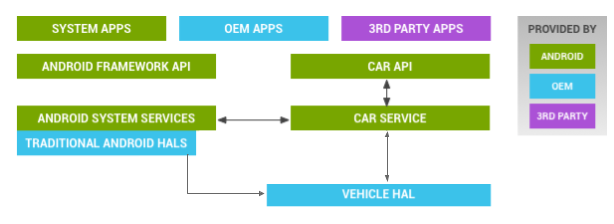
车载HAL与Android Automotive架构:
- Car App:包括OEM和第三方开发的App
- Car API:内有包含CarSensorManager在内的API。位于/platform/packages/services/Car/car-lib
- CarService:系统中与车相关的服务,位于/platform/packages/services/Car/
- Vehicle HAL:汽车的硬件抽象层描述。位于hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/(接口属性:hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/impl/vhal_v2_0/)
1.1.1. Framework CarService
Android O/P为Automotive场景提供了一系列的服务,这些服务统被称为CarService。它们与HAL层的VehicleHAL通信,进而通过车载总线(例如CAN总线)与车身进行通讯,同时它们还为应用层的APP提供接口,从而让APP能够实现对车身的控制与状态的显示
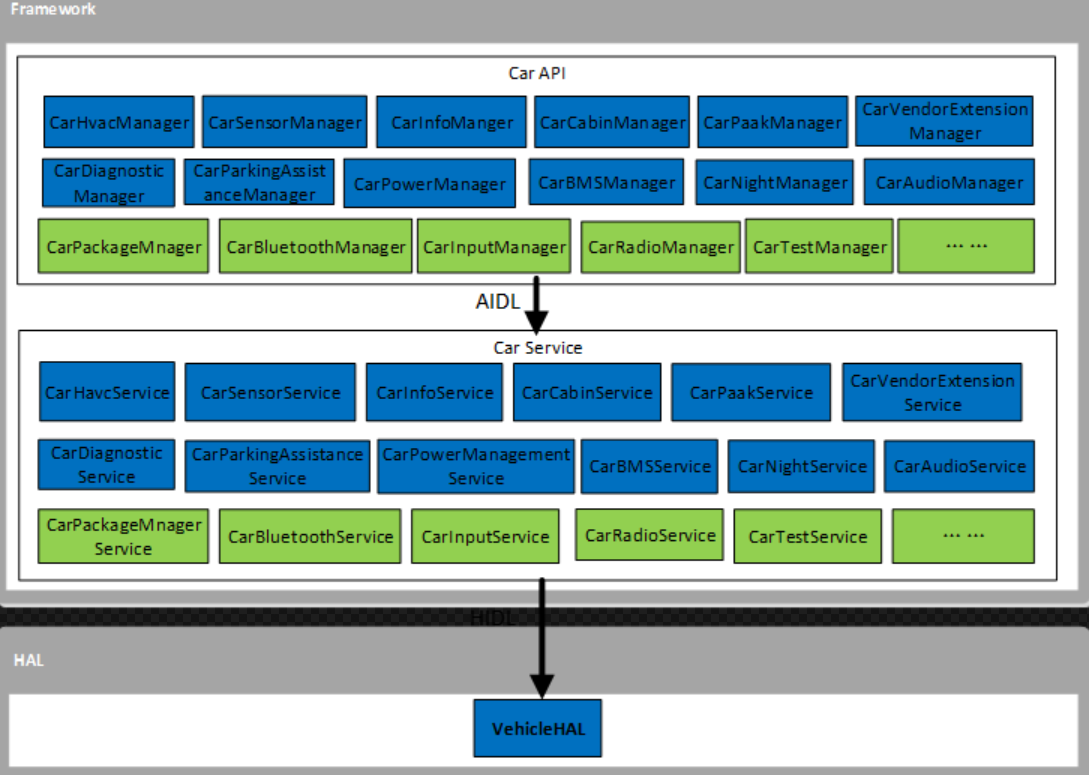
- Car***Manager:
packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/hardware - Car***Service:
packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/
1.2. APP层
1.2.1. APP层确认是否支持车载功能
- APP层在调用Car API之前首先会判断该平台是否支持车载功能:
if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
.....
}
例如:
//packages/apps/SettingsIntelligence/src/com/android/settings/intelligence/suggestions/eligibility/AutomotiveEligibilityChecker.java
public static boolean isEligible(Context context, String id, ResolveInfo info) {
PackageManager packageManager = context.getPackageManager();
//是否支持车载功能
boolean isAutomotive = packageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE);
//是否有车载功能支持的资格
boolean isAutomotiveEligible =
info.activityInfo.metaData.getBoolean(META_DATA_AUTOMOTIVE_ELIGIBLE, false);
if (isAutomotive) {
if (!isAutomotiveEligible) {
Log.i(TAG, "Suggestion is ineligible for FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE: " + id);
}
return isAutomotiveEligible;
}
return true;
}
//frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/pm/PackageManagerService.java
@GuardedBy("mAvailableFeatures")
final ArrayMap<String, FeatureInfo> mAvailableFeatures;
@Override
public boolean hasSystemFeature(String name, int version) {
// allow instant applications
synchronized (mAvailableFeatures) {
final FeatureInfo feat = mAvailableFeatures.get(name);
if (feat == null) {
return false;
} else {
return feat.version >= version;
}
}
}
- 通过Binder访问PackageManagerService,mAvailableFeatures里面的内容是通过读取/system/etc/permissions下面的xml文件(对应SDK的位置—frameworks/native/data/etc下的XML文件中的feature字段)
//frameworks/native/data/etc/car_core_hardware.xml
<permissions>
<!-- Feature to specify if the device is a car -->
<feature name="android.hardware.type.automotive" />
.....
</permission>
//frameworks/native/data/etc/android.hardware.type.automotive.xml
<!-- These features determine that the device running android is a car. -->
<permissions>
<feature name="android.hardware.type.automotive" />
</permissions>
1.2.2. APP创建Car API,接收底层回调
Car作为汽车平台最高等级的API(
packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/Car.java),为外界提供汽车所有服务和数据的访问
- 通过createCar方法可以新建一个Car实例
- 通过connect方法连接CarService
- 当成功连接时可以通过getCarManager方法获取一个一个相关的manager,比如Hvac通过getCarManager方法获取了一个CarHvacManager,当获取到manager后就可以进行相关操作
例如HvacController.java:
//packages/apps/Car/Hvac/src/com/android/car/hvac/HvacController.java
private Object mHvacManagerReady = new Object();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
if (getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
if (SystemProperties.getBoolean(DEMO_MODE_PROPERTY, false)) {
IBinder binder = (new LocalHvacPropertyService()).getCarPropertyService();
initHvacManager(new CarHvacManager(binder, this, new Handler()));
return;
}
//创建Car实例,即new Car对象
mCarApiClient = Car.createCar(this, mCarConnectionCallback);
//connect连接,调用startCarService启动CarService
mCarApiClient.connect();
}
}
private final CarConnectionCallback mCarConnectionCallback =
new CarConnectionCallback() {
@Override
public void onConnected(Car car) {
synchronized (mHvacManagerReady) {
try {
//getCarManager获取manager
//在获取到CarHvacManager后,可以直接调用CarHvacManager提供的接口
//例如mHvacManager.getPropertyList();
initHvacManager((CarHvacManager) mCarApiClient.getCarManager(
android.car.Car.HVAC_SERVICE));
mHvacManagerReady.notifyAll();
} catch (CarNotConnectedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Car not connected in onServiceConnected");
}
}
}
@Override
public void onDisconnected(Car car) {
}
};
private void initHvacManager(CarHvacManager carHvacManager) {
mHvacManager = carHvacManager;
List<CarPropertyConfig> properties = null;
try {
properties = mHvacManager.getPropertyList();
mPolicy = new HvacPolicy(HvacController.this, properties);
//注册回调
mHvacManager.registerCallback(mHardwareCallback);
} catch (android.car.CarNotConnectedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Car not connected in HVAC");
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (mHvacManager != null) {
//取消注册回调
mHvacManager.unregisterCallback(mHardwareCallback);
}
if (mCarApiClient != null) {
mCarApiClient.disconnect();
}
}
//接收处理callback消息
private final CarHvacManager.CarHvacEventCallback mHardwareCallback =
new CarHvacManager.CarHvacEventCallback() {
@Override
public void onChangeEvent(final CarPropertyValue val) {
int areaId = val.getAreaId();
switch (val.getPropertyId()) {
case CarHvacManager.ID_ZONED_AC_ON:
handleAcStateUpdate(getValue(val));
break;
case CarHvacManager.ID_ZONED_FAN_DIRECTION:
handleFanPositionUpdate(areaId, getValue(val));
.....
default:
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Unhandled HVAC event, id: " + val.getPropertyId());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onErrorEvent(final int propertyId, final int zone) {
}
};
例如Radio APP的RadioTunerExt.java文件:
//packages/apps/Car/Radio/src/com/android/car/radio/platform/RadioTunerExt.java
RadioTunerExt(Context context) {
//创建Car实例,即new Car对象
mCar = Car.createCar(context, mCarServiceConnection);
//connect连接,调用startCarService启动CarService
mCar.connect();
}
private final ServiceConnection mCarServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mLock) {
try {
//getCarManager获取manager
mCarAudioManager = (CarAudioManager)mCar.getCarManager(Car.AUDIO_SERVICE);
if (mPendingMuteOperation != null) {
boolean mute = mPendingMuteOperation;
mPendingMuteOperation = null;
Log.i(TAG, "Car connected, executing postponed operation: "
+ (mute ? "mute" : "unmute"));
setMuted(mute);
}
.....
2. 目录结构
2.1. CarService一级目录结构说明(packages/services/Car/)
目录:
packages/services/Car/
.
├── Android.mk
├── apicheck.mk
├── apicheck_msg_current.txt
├── apicheck_msg_last.txt
├── car-cluster-logging-renderer //LoggingClusterRenderingService继承InstrumentClusterRenderingService
├── car-default-input-service //按键消息处理
├── car-lib //提供给汽车App特有的接口,许多定制的模块都在这里实现,包括Sensor,HVAC,Cabin,ActiveParkingAssiance,Diagnostic,Vendor等
├── car-maps-placeholder //地图软件相关
├── car_product //系统编译相关
├── car-support-lib //android.support.car
├── car-systemtest-lib //系统测试相关
├── car-usb-handler //开机自启,用于管理车机USB
├── CleanSpec.mk
├── evs
├── obd2-lib
├── PREUPLOAD.cfg
├── procfs-inspector
├── service //com.android.car是一个后台运行的组件,可以长时间运行并且不需要和用户去交互的,这里即使应用被销毁,它也可以正常工作
├── tests
├── tools //是一系列的工具,要提到的是里面的emulator,测试需要用到的。python写的,通过adb可以连接vehicleHal的工具,用于模拟测试
├── TrustAgent
└── vehicle-hal-support-lib
2.2. Car APP
packages/services/Car/car_product/build/car.mk里面决定了是否编译相关apk(system/priv-app)- 源码位置::
packages/apps/Car/
这个文件中列出了汽车系统中的专有模块(首字母大写的模块基本上都是汽车系统中专有的App):
//packages/services/Car/car_product/build/car.mk
# Automotive specific packages
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
CarService \
CarTrustAgentService \
CarDialerApp \ # 电话应用,包含拨号键盘、通话记录等
CarRadioApp \ # 收音机应用
OverviewApp \
CarLauncher \
CarLensPickerApp \ # 活动窗口选择应用(Launcher)
LocalMediaPlayer \ # 提供本地播放服务的应用
CarMediaApp \ # 媒体应用,包含播放界面等
CarMessengerApp \ # 消息管理应用,包含消息及TTS相关功能
CarHvacApp \ # 空调应用,空调显示及操作界面
CarMapsPlaceholder \
CarLatinIME \ # 输入法应用
CarSettings \ # 设置应用
CarUsbHandler \
android.car \
car-frameworks-service \
com.android.car.procfsinspector \
libcar-framework-service-jni \
....
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += \
Bluetooth \
OneTimeInitializer \
Provision \
SystemUI \
SystemUpdater # 系统升级应用
2.3. Car API
- 源码位置:
/platform/packages/services/Car/car-lib,因为对手机和平板没有意义,仅用于开发汽车,所以没有包含在Framework SDK中
Car API(详细路径:packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/)有如下:
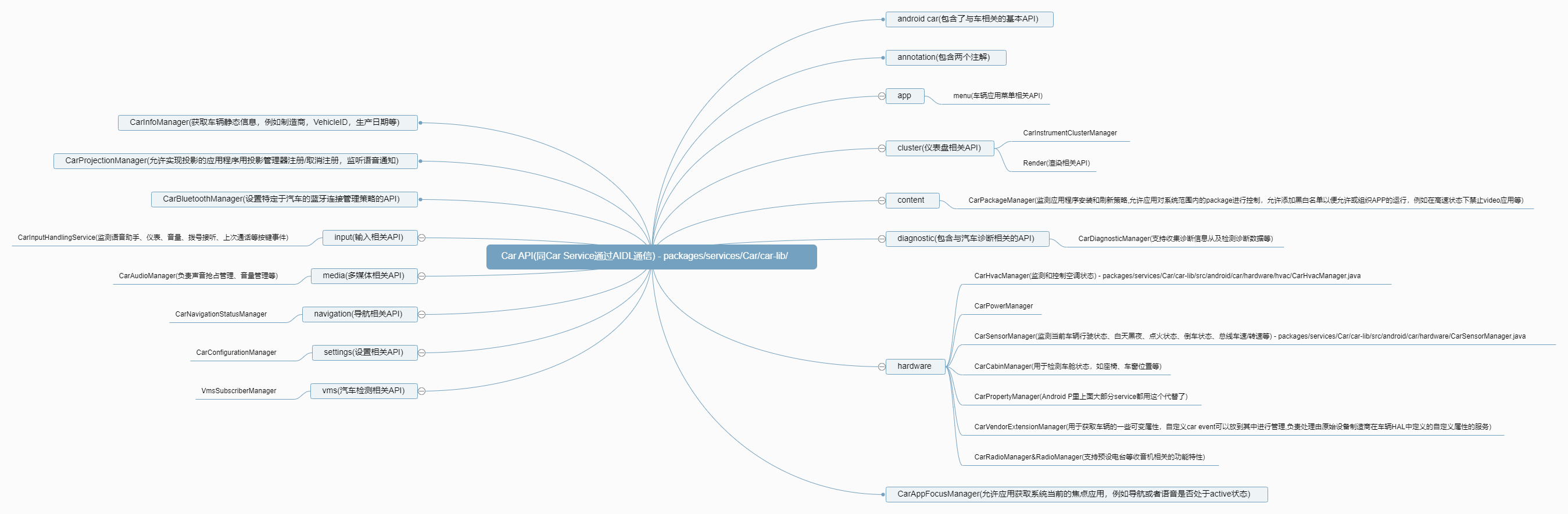
Car API类图:
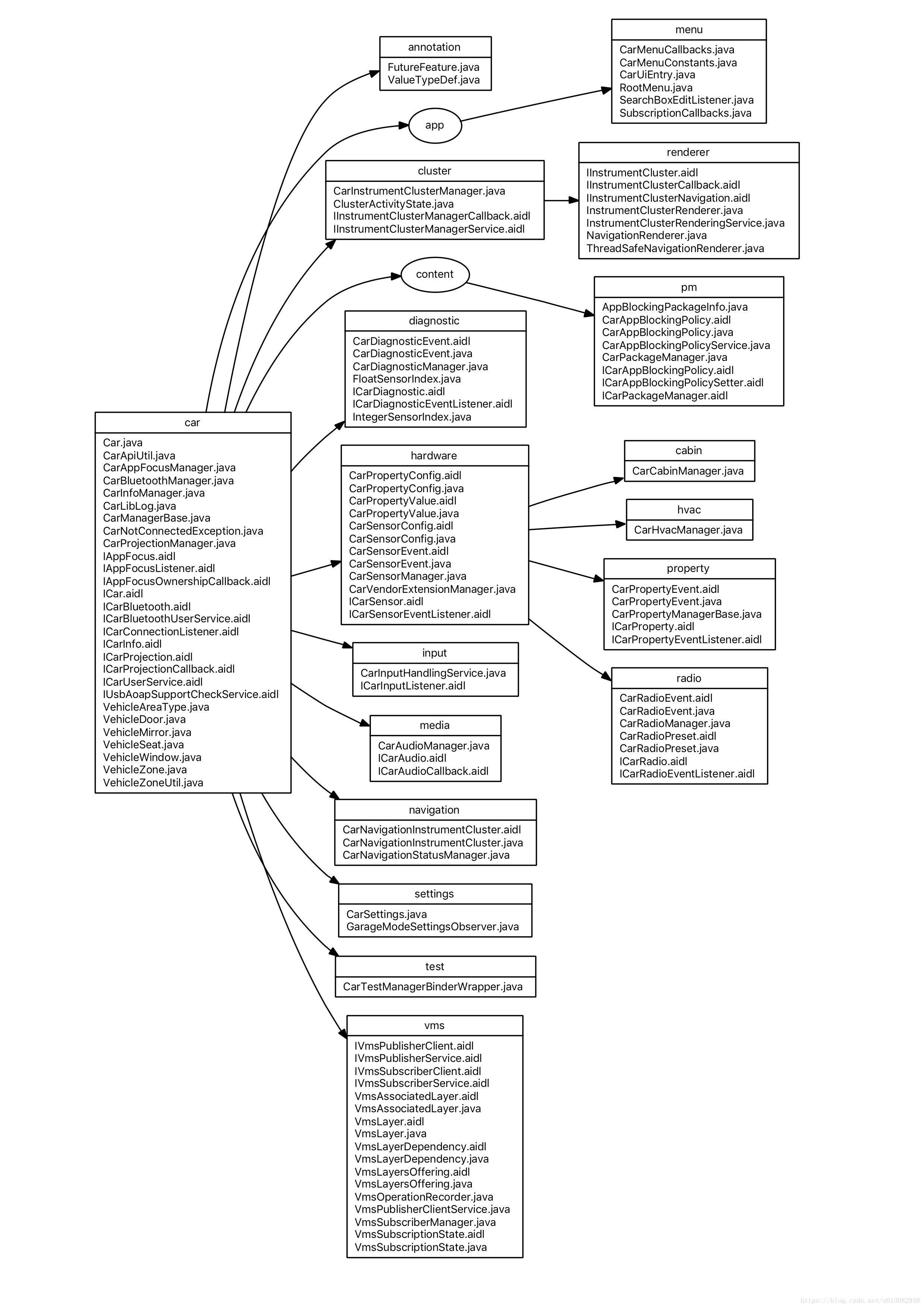
2.4. Car Service
- 源码位置:
packages/services/Car/
CarServcie模块与很多模块都需要交互(供参考):
- 向上给APP提供API接口;
- 向下与MCU进行通信,进而和车身网络进行交互;
- 给其他模块提供标定项信息;
- 给Camera模块提供Digital RVC控制信息等;
- 可以获取DSP版本、前屏版本号等;
- 持有Power模块的锁,carservice挂了就会息屏

2.5. AIDL
Android接口定义语言,一种android内部进程通信接口的描述语言,通过它我们可以定义进程间的通信接口
如要使用 AIDL 创建绑定服务,请执行以下步骤:
- 创建
.aidl文件:此文件定义带有方法签名的编程接口 - 实现接口:Android SDK 工具会基于您的
.aidl文件,使用Java编程语言生成接口。此接口拥有一个名为Stub的内部抽象类,用于扩展Binder类并实现AIDL接口中的方法您必须扩展Stub类并实现这些方法 - 向客户端公开接口,实现Service并重写
onBind(),从而返回Stub类的实现
2.5.1. 示例ICarInputListener
- AIDL文件:
//packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/input/ICarInputListener.aidl /** * Binder API for Input Service. * * @hide */ oneway interface ICarInputListener { /** Called when key event has been received. */ void onKeyEvent(in KeyEvent keyEvent, int targetDisplay) = 1; } - 同目录下实现AIDL接口中的内部抽象类Stub(Stub类继承了Binder,并继承我们在aidl文件中定义的接口)
//packages/services/Car/car-lib/src/android/car/input/CarInputHandlingService.java
private class InputBinder extends ICarInputListener.Stub {
private final EventHandler mEventHandler;
InputBinder() {
mEventHandler = new EventHandler(CarInputHandlingService.this);
}
@Override
public void onKeyEvent(KeyEvent keyEvent, int targetDisplay) throws RemoteException {
mEventHandler.doKeyEvent(keyEvent, targetDisplay);
}
}
- 客户端调用服务端的aidl描述的接口对象
PS:如果需要返回对象则需要实现Service.onBind(Intent)方法,该方法会返回一个IBinder对象到客户端
//packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarInputService.java
private final ServiceConnection mInputServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder) {
if (DBG) {
Log.d(CarLog.TAG_INPUT, "onServiceConnected, name: "
+ name + ", binder: " + binder);
}
mCarInputListener = ICarInputListener.Stub.asInterface(binder);
try {
binder.linkToDeath(() -> CarServiceUtils.runOnMainSync(() -> {
Log.w(CarLog.TAG_INPUT, "Input service died. Trying to rebind...");
mCarInputListener = null;
// Try to rebind with input service.
mCarInputListenerBound = bindCarInputService();
}), 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(CarLog.TAG_INPUT, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
2.6. carservice启动流程
大致流程:
- SystemServer启动CarServiceHelperService服务
- 在调用startService后,CarServiceHelperService的onStart方法通过bindService的方式启动CarService(一个系统级别的APK,位于system/priv-app)
- 启动CarService后首先调用onCreate,创建ICarImpl对象并初始化,在此时创建了一系列car相关的核心服务,并遍历init初始化
- 然后调用onBind将该ICarImpl对象返回给CarServiceHelperService,CarServiceHelperService在内部的一个Binder对象ICarServiceHelperImpl传递给CarService,建立双向跨进程
2.6.1. 序列图
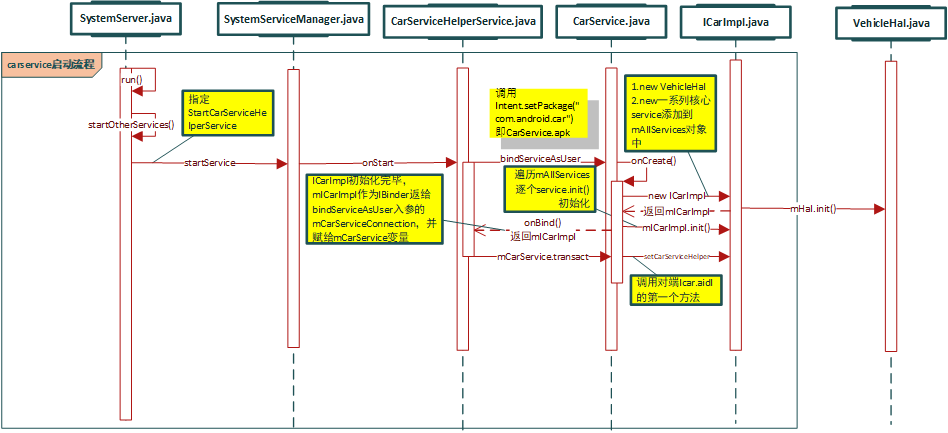
2.6.2. 启动CarServiceHelperService服务
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java - run() —-> startOtherServices()
private static final String CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS =
"com.android.internal.car.CarServiceHelperService";
......
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartCarServiceHelperService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CAR_SERVICE_HELPER_SERVICE_CLASS);
traceEnd();
}
—–> frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java - startService
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public SystemService startService(String className) {
....
return startService(serviceClass);
}
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
...
startService(service);
...
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
......
try {
service.onStart();
...
}
2.6.3. 绑定carservice服务
—–> frameworks/opt/car/services/src/com/android/internal/car/CarServiceHelperService.java - onStart()
//这就是系统中和汽车相关的核心服务CarService,相关源代码在packages/services/Car/service目录下
private static final String CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE = "android.car.ICar";
@Override
public void onStart() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setPackage("com.android.car"); //绑定包名,设置广播仅对该包有效
//绑定action,表明想要启动能够响应设置的这个action的活动,并在清单文件AndroidManifest.xml中设置action属性
intent.setAction(CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE);
//绑定后回调
if (!getContext().bindServiceAsUser(intent, mCarServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
UserHandle.SYSTEM)) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "cannot start car service");
}
System.loadLibrary("car-framework-service-jni");
}
- service源码路径:packages/services/Car/service/AndroidManifest.xml
sharedUserId是系统级别的,类似SystemUI,它编译出来同样是一个APK文件
设备文件路径在: /system/priv-app/CarService/CarService.apk
//packages/services/Car/service/AndroidManifest.xml
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:androidprv="http://schemas.android.com/apk/prv/res/android"
package="com.android.car"
coreApp="true"
android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system">
......
<application android:label="Car service"
android:directBootAware="true"
android:allowBackup="false"
android:persistent="true">
<service android:name=".CarService"
android:singleUser="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.car.ICar" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
<service android:name=".PerUserCarService" android:exported="false" />
</application>
2.6.4. bindService启动流程
context.bindService() ——> onCreate() ——> onBind() ——> Service running ——> onUnbind() ——> onDestroy() ——> Service stop
onBind()将返回给客户端一个IBind接口实例,IBind允许客户端回调服务的方法,比如得到Service的实例、运行状态或其他操作。这个时候把调用者(Context,例如Activity)会和Service绑定在一起,Context退出了,Srevice就会调用onUnbind->onDestroy相应退出。
所以调用bindService的生命周期为:onCreate --> onBind(只一次,不可多次绑定) --> onUnbind --> onDestroy
在Service每一次的开启关闭过程中,只有onStart可被多次调用(通过多次startService调用),其他onCreate,onBind,onUnbind,onDestroy在一个生命周期中只能被调用一次
2.7. Car Service启动
2.7.1. onCreate
——–> packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarService.java - onCreate()
创建ICarImpl实例
@Nullable
private static IVehicle getVehicle() {
try {
//该service启动文件hardware/interfaces/automotive/vehicle/2.0/default/android.hardware.automotive.vehicle@2.0-service.rc
return android.hardware.automotive.vehicle.V2_0.IVehicle.getService();
} ....
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(CarLog.TAG_SERVICE, "Service onCreate");
//获取hal层的Vehicle service
mVehicle = getVehicle();
//创建ICarImpl实例
mICarImpl = new ICarImpl(this,
mVehicle,
SystemInterface.Builder.defaultSystemInterface(this).build(),
mCanBusErrorNotifier,
mVehicleInterfaceName);
//然后调用ICarImpl的init初始化方法
mICarImpl.init();
//设置boot.car_service_created属性
SystemProperties.set("boot.car_service_created", "1");
linkToDeath(mVehicle, mVehicleDeathRecipient);
//最后将该service注册到ServiceManager
ServiceManager.addService("car_service", mICarImpl);
super.onCreate();
}
//packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/ICarImpl.java
private final VehicleHal mHal;
//构造函数启动一大堆服务
public ICarImpl(Context serviceContext, IVehicle vehicle, SystemInterface systemInterface,
CanBusErrorNotifier errorNotifier, String vehicleInterfaceName) {
mContext = serviceContext;
mSystemInterface = systemInterface;
//创建VehicleHal对象
mHal = new VehicleHal(vehicle);
mVehicleInterfaceName = vehicleInterfaceName;
mSystemActivityMonitoringService = new SystemActivityMonitoringService(serviceContext);
mCarPowerManagementService = new CarPowerManagementService(mContext, mHal.getPowerHal(),
systemInterface);
mCarPropertyService = new CarPropertyService(serviceContext, mHal.getPropertyHal());
.....
//InstrumentClusterService service启动
mInstrumentClusterService = new InstrumentClusterService(serviceContext,
mAppFocusService, mCarInputService);
mSystemStateControllerService = new SystemStateControllerService(serviceContext,
mCarPowerManagementService, mCarAudioService, this);
mPerUserCarServiceHelper = new PerUserCarServiceHelper(serviceContext);
// mCarBluetoothService = new CarBluetoothService(serviceContext, mCarPropertyService,
// mPerUserCarServiceHelper, mCarUXRestrictionsService);
mVmsSubscriberService = new VmsSubscriberService(serviceContext, mHal.getVmsHal());
mVmsPublisherService = new VmsPublisherService(serviceContext, mHal.getVmsHal());
mCarDiagnosticService = new CarDiagnosticService(serviceContext, mHal.getDiagnosticHal());
mCarStorageMonitoringService = new CarStorageMonitoringService(serviceContext,
systemInterface);
mCarConfigurationService =
new CarConfigurationService(serviceContext, new JsonReaderImpl());
mUserManagerHelper = new CarUserManagerHelper(serviceContext);
//注意排序,service存在依赖
List<CarServiceBase> allServices = new ArrayList<>();
allServices.add(mSystemActivityMonitoringService);
allServices.add(mCarPowerManagementService);
allServices.add(mCarPropertyService);
allServices.add(mCarDrivingStateService);
allServices.add(mCarUXRestrictionsService);
allServices.add(mCarPackageManagerService);
allServices.add(mCarInputService);
allServices.add(mCarLocationService);
allServices.add(mGarageModeService);
allServices.add(mAppFocusService);
allServices.add(mCarAudioService);
allServices.add(mCarNightService);
allServices.add(mInstrumentClusterService);
allServices.add(mCarProjectionService);
allServices.add(mSystemStateControllerService);
// allServices.add(mCarBluetoothService);
allServices.add(mCarDiagnosticService);
allServices.add(mPerUserCarServiceHelper);
allServices.add(mCarStorageMonitoringService);
allServices.add(mCarConfigurationService);
allServices.add(mVmsSubscriberService);
allServices.add(mVmsPublisherService);
if (mUserManagerHelper.isHeadlessSystemUser()) {
mCarUserService = new CarUserService(serviceContext, mUserManagerHelper);
allServices.add(mCarUserService);
}
mAllServices = allServices.toArray(new CarServiceBase[allServices.size()]);
}
@MainThread
void init() {
traceBegin("VehicleHal.init");
mHal.init();
traceEnd();
traceBegin("CarService.initAllServices");
//启动的所有服务遍历调用init初始化(各个都继承了CarServiceBase)
for (CarServiceBase service : mAllServices) {
service.init();
}
traceEnd();
}
2.7.2. onBind
将上面onCreate创建的mICarImpl对象返回:
- onBind()回调方法会继续传递通过bindService()传递来的intent对象(即上面的
bindServiceAsUser方法) - onUnbind()会处理传递给unbindService()的intent对象。如果service允许绑定,onBind()会返回客户端与服务互相联系的通信句柄
//packages/services/Car/service/src/com/android/car/CarService.java
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mICarImpl;
}
所以此处的mICarImpl会作为IBinder返回给CarServiceHelperService.java - bindServiceAsUser方法中的参数mCarServiceConnection(回调)
2.7.3. onDestroy
释放mICarImpl创建的资源,包含一系列的服务:
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(CarLog.TAG_SERVICE, "Service onDestroy");
mICarImpl.release();
mCanBusErrorNotifier.removeFailureReport(this);
if (mVehicle != null) {
try {
mVehicle.unlinkToDeath(mVehicleDeathRecipient);
mVehicle = null;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Ignore errors on shutdown path.
}
}
super.onDestroy();
}
2.8. 回调ServiceConnection
ICarImpl初始化完毕,会作为IBinder返回给
CarServiceHelperService.java - bindServiceAsUser方法中绑定此服务的mCarServiceConnection(回调)
mCarServiceConnection初始化如下:
- 其中返回的ICarImpl被保存在了CarServiceHelperService的mCarService
- mCarService.transact跨进程通信,调用ICar.aidl中定义的第一个方法setCarServiceHelper
//frameworks/opt/car/services/src/com/android/internal/car/CarServiceHelperService.java
private static final String CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE = "android.car.ICar";
private IBinder mCarService;
private final ICarServiceHelperImpl mHelper = new ICarServiceHelperImpl();
private final ServiceConnection mCarServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
Slog.i(TAG, "**CarService connected**");
//1. 返回的ICarImpl被保存在了CarServiceHelperService的mCarService
mCarService = iBinder;
// Cannot depend on ICar which is defined in CarService, so handle binder call directly
// instead.
// void setCarServiceHelper(in IBinder helper)
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(CAR_SERVICE_INTERFACE);
//将ICarServiceHelperImpl类型的对象作为数据跨进程传递
data.writeStrongBinder(mHelper.asBinder());
try {
//2.跨进程传输
//对端是mCarService即ICarImpl,调用binder的transact进行跨进程通信
//其code代表需要调用的对端方法,data为携带的传输数据
//FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION = 0x00000001,即调用对端ICar.aidl中定义的第一个方法setCarServiceHelper
mCarService.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // setCarServiceHelper
data, null, Binder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "RemoteException from car service", e);
handleCarServiceCrash();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
handleCarServiceCrash();
}
};
2.9. 跨进程setCarServiceHelper
@Override
public void setCarServiceHelper(IBinder helper) {
int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
if (uid != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
throw new SecurityException("Only allowed from system");
}
synchronized (this) {
//将ICarServiceHelper的代理端保存在ICarImpl内部mICarServiceHelper
mICarServiceHelper = ICarServiceHelper.Stub.asInterface(helper);
//同时也传给了SystemInterface
//此时他们有能力跨进程访问CarServiceHelperService
mSystemInterface.setCarServiceHelper(mICarServiceHelper);
}
}
3. 参考
Android Automotive之CarService开机启动
深入理解Android的startservice和bindservice
Leave a comment